How to Manage Acne in Newborns: A Guide for Parents
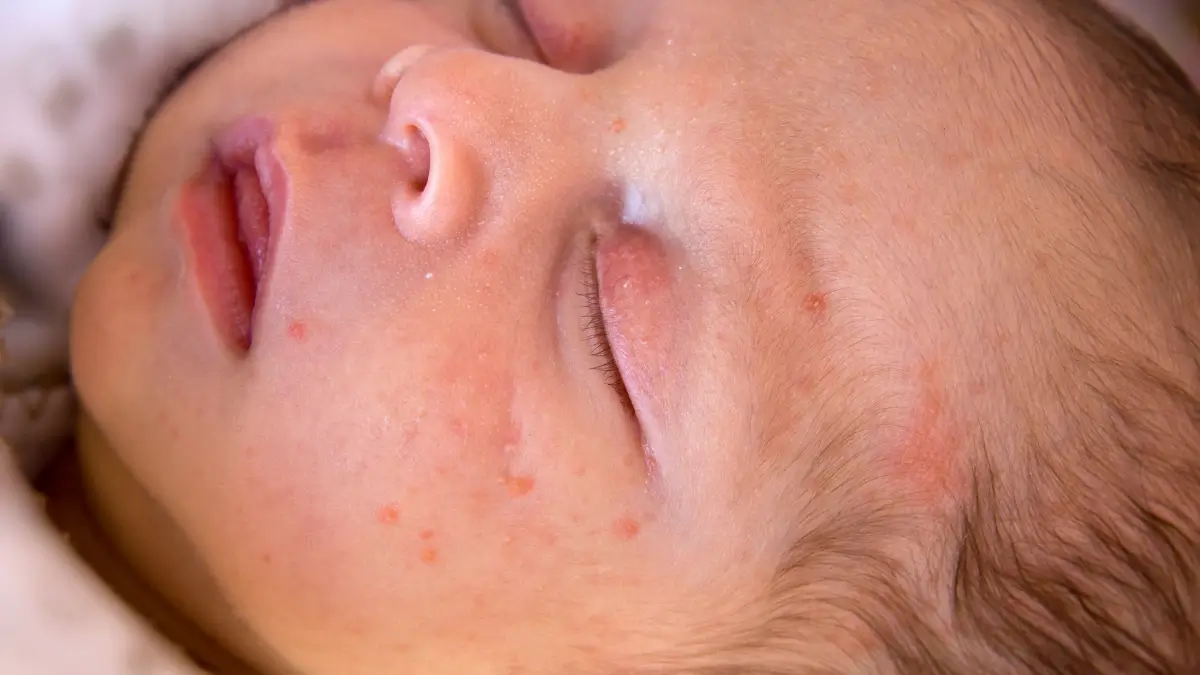
Neonatal acne, affecting about 20% of newborns, typically appears around 2 weeks of age, although it can manifest anytime before 6 weeks. In some cases, babies are born with this condition.
The most common areas for these breakouts are the baby’s cheeks and nose, but they can also appear on the forehead, chin, scalp, neck, back, or chest.
Is Baby Acne Dangerous?
Fortunately, neonatal acne is usually harmless. It rarely leads to scarring and typically resolves within a few weeks to a few months without any treatment.
Neonatal Acne vs. Infantile Acne
It’s important to distinguish between neonatal acne and infantile acne. The latter usually starts between 3 and 6 months of age. Unlike neonatal acne, infantile acne can sometimes lead to scarring and may require treatment to prevent long-term skin damage.
When Should You Worry?
If acne develops after 6 weeks, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist or pediatrician. This late-onset acne could be mistaken for other skin conditions like eczema or a skin infection and, in rare cases, might signal an underlying health issue. A thorough skin examination and possibly a blood test might be necessary.
Manage Baby Acne
Identify Potential Triggers: Assess if the acne is a reaction to skin products. Ointments or oils in some products can trigger acne.
Avoid Permanent Scars: While neonatal acne rarely causes scars, the risk is higher with infantile acne. A dermatologist can guide you in preventing scarring.
Patience is Key: Most baby acne cases clear up on their own, typically within 6 months to a year. However, some children may experience acne for a longer duration.
Following are some tips for your baby’s Skin:
- Avoid Adult Acne Treatments: Never use adult acne treatments on your baby’s skin, unless recommended by a healthcare professional.
- Gentle Skin Care: Handle your baby’s skin with care, avoiding any scrubbing or harsh treatments.
- Lukewarm Baths: Use lukewarm water for bathing your baby, avoiding hot water.
- Review Skin Care Products: Discontinue using any oily or greasy products on your baby’s skin.
Prevention Strategies
- Regular Pediatric Check-ups: Regular visits to the pediatrician can help monitor and manage any skin issues effectively.
- Careful Observation: Keep an eye on any changes in your baby’s skin and consult a healthcare provider if acne persists or worsens.
- Skin-friendly Products: Choose baby products designed for sensitive skin, free from harsh chemicals and fragrances.
In summary, while neonatal acne is a common and mostly benign condition, understanding its characteristics and knowing when to seek medical advice is key. With the right care and attention, your baby’s skin can remain healthy and clear. Remember, every baby is unique, and what works for one might not work for another.
When in doubt, always consult with a healthcare professional.